Nutrition
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
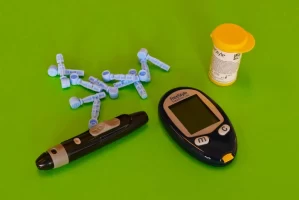
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by elevated blood sugar levels and impaired carbohydrate metabolism. The signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop slowly and often go undetected in the initial stages. However, early detection of the disease is crucial for its effective control and prevention of complications.
One of the most characteristic symptoms of type 2 diabetes is increased thirst. People with this condition often experience high fluid intake, which is associated with elevated blood sugar levels, which causes excess fluid to be excreted through urine. This, in turn, can lead to frequent urination, which is also a common symptom.
Fatigue and weakness are other common symptoms of type 2 diabetes. As it becomes more difficult for the body's cells to metabolize glucose, they do not receive enough energy, which causes a general feeling of fatigue and decreased performance.
Changes in weight may also indicate diabetes. In some cases, people experience sudden weight loss despite a normal or increased appetite, while others may experience weight gain. This is due to the fact that the body begins to use fats and muscles for energy when glucose cannot be absorbed normally.
Additionally, it should be noted that type 2 diabetes can cause skin problems such as itching or frequent infections. There may also be pain and numbness in the limbs due to nerve damage, called diabetic neuropathy. Other symptoms may include blurred vision and slow wound healing.
It is important to remember that many of these symptoms can occur in other conditions, but if you have several of them, it is recommended to see a doctor to check your blood sugar levels. Early treatment and diagnosis can help avoid serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney problems and vision problems. Controlling blood sugar levels, lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication can significantly improve the quality of life for people with type 2 diabetes.