Basic terms for type 2 diabetes
1. General concepts
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease in which the body ineffectively uses insulin (insulin resistance) or does not produce enough of it.
Glucose is the main source of energy for cells, the level of which in the blood needs to be controlled.
Insulinis a pancreatic hormone that helps glucose enter cells.
Hyperglycemia—high blood sugar (above 7 mmol/l on an empty stomach).
Hypoglycemia – low sugar level (below 3.9 mmol/l), a dangerous condition.
HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin) – an indicator of the average sugar level over the last 2-3 months (normal < 5.7%, with diabetes ≥ 6.5%).
2. Diagnostics and control
Insulin resistance — a decrease in the sensitivity of cells to insulin.
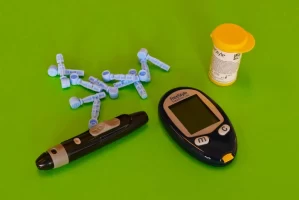
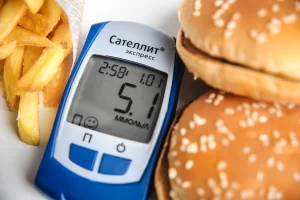
Glucometer — a device for measuring blood glucose levels.
C-peptide — an indicator of the production of your own insulin.
Postprandial glycemia — sugar level 2 hours after eating.
3. Complications
Diabetic neuropathy – nerve damage (numbness, pain in the limbs).
Retinopathy – damage to the retinal vessels leading to blindness.
Nephropathy – damage to the kidneys.
Diabetic foot – ulcers and infections of the feet due to poor circulation.
4. Treatment
Metformin is a first-line drug to reduce insulin resistance.
Sulfonylureas — stimulate insulin production (for example, glibenclamide).
GLP-1 agonists(liraglutide) — reduce appetite and sugar.
SGLT2 inhibitors(dapagliflozin) — remove glucose through the kidneys.
5. Lifestyle
Low-carbohydrate diet — food with a restriction of fast carbohydrates.
Glycemic index (GI) — an indicator of the effect of food on sugar levels.
Ketoacidosis — a dangerous condition when a sharp increase in ketones in the blood (rarely in type 2).
6. Additional terms
Metabolic syndrome – a combination of obesity, hypertension and insulin resistance.
Prediabetes – borderline state (HbA1c 5.7–6.4%).
Basal insulin – long-acting to maintain background levels.
Knowing these terms will help you better understand your disease and manage your diabetes more effectively! 📚💙